Google changes documentation on crawling and robots.txt
Google has updated the crawl status report documentation. According to this, if robots.txt is not available, Google will stop crawling after 30 days if the homepage of a website cannot be reached.
There are a number of interesting changes to Google’s documentation on the Search Console crawl status report. It is now even clearer how Google reacts in the event of an unreachable robots.txt and what the consequences are for crawling. There are also some important changes in how Googlebot responds. Spotted and shared on Twitter by SEO Brodie Clark:
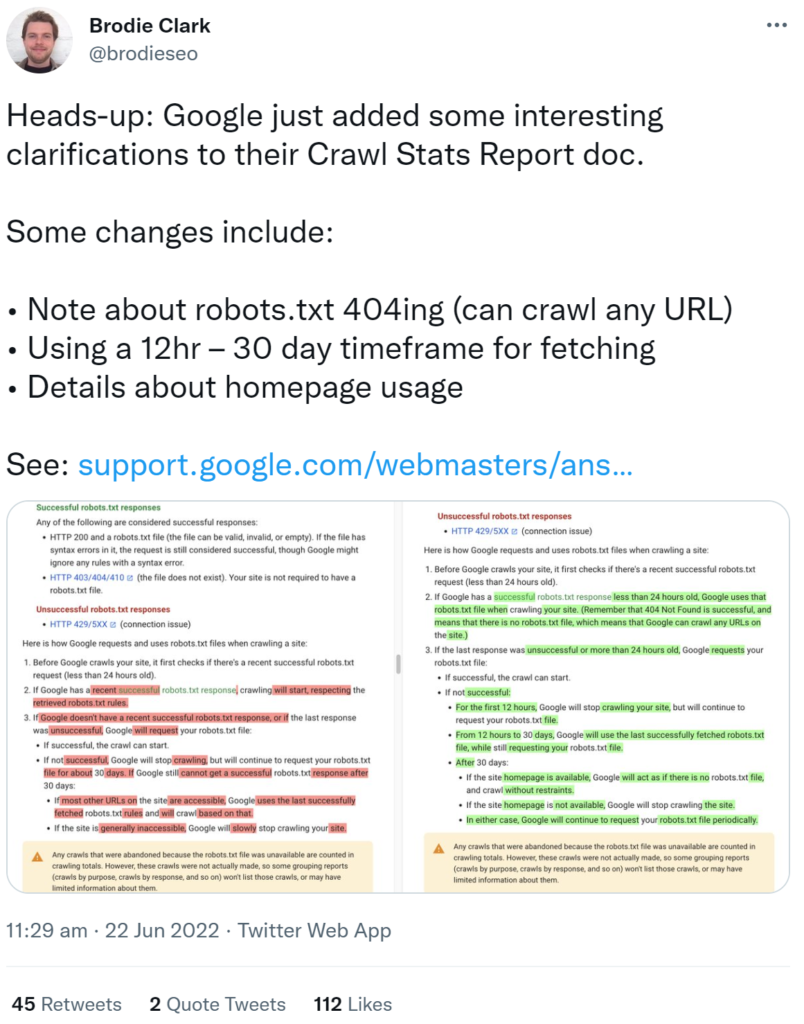
The most important changes in the documentation are summarized below:
If Google has received a successful response to the robots.txt request that is more recent than 24 hours, then Google uses this robots.txt for crawling (the period of 24 hours has been added). The note was also added that a 404 when retrieving robots.txt is considered a successful retrieval. This is treated as if there were no robots.txt. Google can use it to crawl any URL on the website.
The following periods are also new: If robots.txt is not successfully retrieved, Google will stop crawling the website for 12 hours. After 12 hours and up to 30 days, Google will use the last successfully retrieved robots.txt to crawl. After 30 days, Google will crawl the entire site if the home page is available and act as if there is no robots.txt. If the site’s home page is not available, Google will stop crawling the site. However, Google will continue to attempt to retrieve the robots.txt on a regular basis.
Previously it was said that Google would crawl a website with unavailable robots.txt after 30 days if most of the website’s URLs were available. The last successfully retrieved robots.txt would be used.
In contrast to a 404, a 403 does not count as a successful retrieval of a robots.txt. This also and especially applies to 500 errors.



